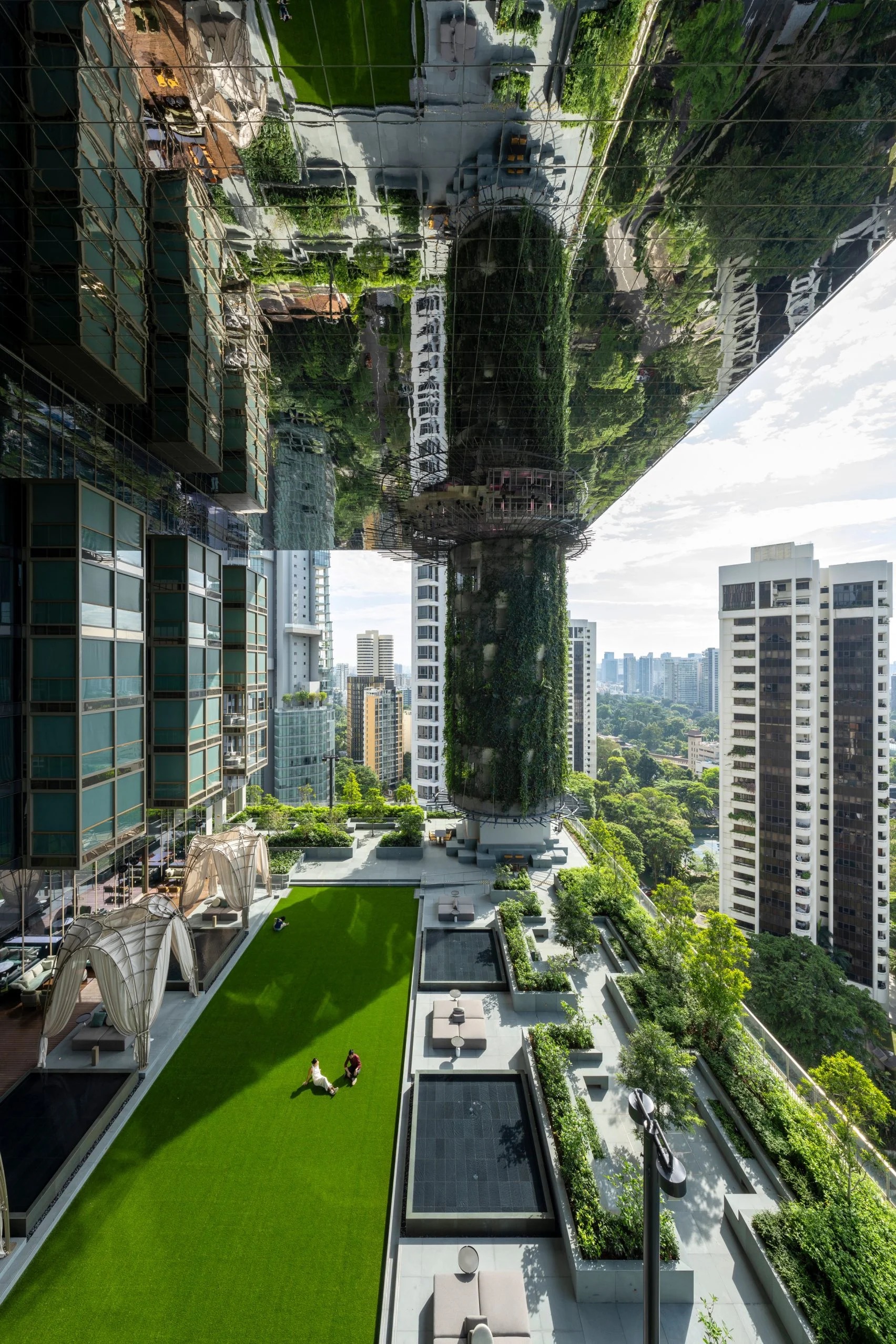
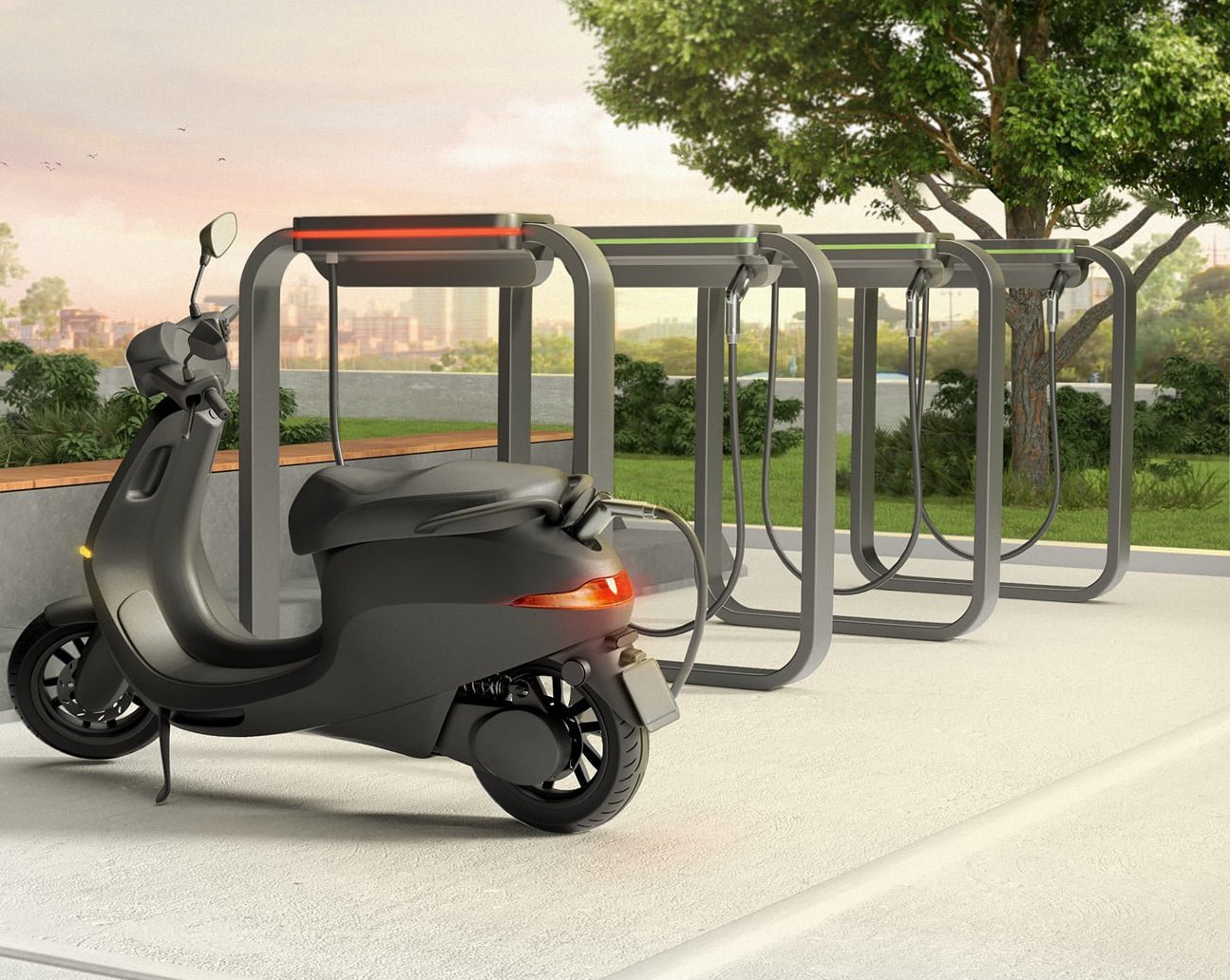
Technology has also played a crucial role in promoting sustainable design practices in architecture.
Architects can use specialized software to analyze the environmental impact of their designs at each stage of the project.
This includes assessing factors such as energy consumption, material selection, and waste management.
By integrating sustainability into their designs from the start, architects can create buildings that are energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
SUSTAINABILITY IN INDUSTRIAL DESIGN:
CONCEPTS, CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES
Martina Keitsch*
Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Norway
ABSTRACT
Design is often associated with making good looking, expensive products. However,
as the Rio Declaration in 2005 states, designers can also contribute to a better life-quality
in society. Meeting sustainability, industrial design is called upon to create ecological and
user-friendly products and services, considering various technical and functional levels
such as minimizing the negative environmental impact by enhancing efficiency and
moderating the use of materials, energy, and development space. Measures and tools to
relate the design solution to the climate, the region, and cultural conditions seem equally
important. In order to establish harmonious interactions between users and
products/services, good form-giving is essential too – ‘green’ products should be well
designed, easy to use and beautiful.
The proposed chapter takes a systematic account of some key concepts of
sustainability in industrial design, discussing knowledge generated and lessons learned.
Examples and methods of how designers contribute to a sustainable development are
presented and opportunities and challenges analyzed. Changes towards sustainability
already appeared in the early 1980’s, when the manufacturing industry started with
cleaner production strategies. This approach moved forward through a life cycle
assessment to ‘design for the environment’. Today, sustainability in industrial design is
represented by concepts such as ‘eco-design’ and ‘industrial ecology’ however a change
towards ‘design for sustainability’ as a model for the future has started. An important
feature of design for sustainability is an approach wherein greater emphasis is placed on a
‘user centered approach’ in order to elaborate sustainable design solutions with involved
stakeholders. The chapter will conclude with a discussion on opportunities and challenges
for industrial design and an outlook on how design for sustainability concepts can,
besides ecological advantages, work as catalysts for the advancement of social sustainability – guided by the principle that a design solution is not truly considered
sustainable until it is accessible.